I hail from a lineage of architects and spent my childhood immersed in the world of steel and concrete crafted by my father, fostering a deep-seated passion for architectural design. As our society leaps forward and aspirations for a better lifestyle rise, I began to dream up a concept for a house that embodies efficiency, ecology, intelligence, sharing, and cultural richness. This home would not only offer a comfortable living experience but also blend cutting-edge technology with environmental sustainability. This concept inspired my design of the smart city sandbox model.
Project Introduction:
Transformable City Homes – Smart Community Design
Design Concept:
By integrating green ecology with smart technology, and incorporating the concepts of open communities, green communities, smart communities, and humanistic communities, this design aims to create a flexible living environment that adapts to various natural climates. It allows green elements to truly permeate every detail of daily life.
Open Community
With smart access control, the community eliminates the need for enclosing walls, allowing the urban landscape to blend seamlessly with the community landscape. It achieves the concept of a home within a park, where residents navigate through an urban forest.
Green Community
- New energy sources such as solar and wind power enable the community to be self-sufficient in energy while also providing the possibility to return energy to the national grid, bringing additional economic income to residents.
- Convenient management services for electric vehicles, with 100% of parking spaces equipped with charging stations with a scheduled charging function (charging at night to avoid peak electricity usage hours, enhancing grid efficiency, and reducing peak period grid pressure); installation of energy storage systems in parking areas (stored electricity from off-peak periods to supplement peak demand, thus reducing grid pressure during peak times); sharing of charging stations and parking spaces (sharing with temporary vehicles when owners are not home) and separation of vehicle and pedestrian traffic (separating vehicle traffic from residential activity areas to ensure the safety of the elderly and children within the community).
- Integration of vertical greening to achieve multi-level and multi-dimensional urban green spaces, creating vertical forests, and implementing rainwater collection and irrigation systems.
- Light-guiding illumination with fiber optic technology to bring natural light indoors and illuminate underground parking areas.
- Fresh air ventilation systems
Smart Community
- Rotatable houses, like sunflowers chasing the sun, ensure ample daylight and sunlight exposure.
- Intelligent landscaping system that automatically adjusts the landscape space according to the seasons, such as transforming a summer rain corridor into a sunny winter gallery, an expansive water feature in the summer into an ice and snow playground in the winter, a well-ventilated environment in the summer, and adjustable landscape walls to block the cold northwest winds in the winter.
- In-home garbage sorting system to facilitate resource recycling;
- Smart parcel lockers: located in centralized areas of the community or at each household’s doorstep, allowing couriers to open the locker by scanning a code to complete deliveries.
- Environmental sensors: door and window sensors, smoke sensors, natural gas sensors, air quality sensors, water immersion sensors, etc., all interconnected with environmental facilities.
Humanistic Community
- Care system: Elderly and children wear care bracelets with AI technology to record location information within the community through an indoor positioning system, learning the wearer’s activity patterns, and monitoring the care recipient’s state of activity based on bracelet data. Integrated with a video monitoring system, if someone remains stationary for a long time in areas like stairwells, it could indicate a fall or a need for urgent care, automatically reporting the situation to the community management system.
- Community facilities for all ages: The community is equipped with facilities suitable for all ages, including kindergartens, elder care facilities, and a health advisory system, ensuring joy for the young and support for the elderly and achieving a harmonious society.
- Emphasis on community cultural development: Various community interaction spaces are established, including children’s playgrounds, fitness plazas, pet parks, jogging tracks, art galleries, and community clubs, aiming to break away from the pattern of a society of strangers and return to a warm neighborhood of familiar relationships.
The following content is a paper written for this project.
Smart City, Thriving in Light
Author: Gary Hua
Beijing Jingshan School
Abstract: As urbanization in China continues to increase, urban development is accelerating, and various urban issues are emerging as a result, such as population surges, environmental degradation, and ecological imbalances. These social and environmental issues necessitate the urgent integration of urban development with new scientific and technological advancements to find a new path to sustainable development. With advanced information technology to synthesize existing urban system elements, the construction of a smart city that meets the requirements of sustainable development and ensures the harmonious coexistence of humans and nature is imperative. This design proposal aims to address the current residential issues of city dwellers and proposes new ideas for building green new towns and intelligent living. The design adopts the latest prefabricated technology, intelligent technology systems, mature building structures, and cutting-edge urban development and sharing theories to provide a more efficient, green, and intelligent planning and design for urban transformation.
Keywords: Smart Cities, Green Cities, Work-Life Balance, Prefabricated Buildings, Rotatable Buildings, Pedestrian and Vehicle Separation, Modular Buildings, Parking Buildings
1 Introduction
Urban construction requires a global vision, international standards, Chinese characteristics, and high positioning, and should be a new type of city that is green, smart, efficient, and livable [1]. The development of new smart cities must pay close attention to the leading and driving role of informatization in urban planning, design, and construction [2] ; Harvard Business School advocates in the “Smart City Manifesto” that smart cities and intelligent communities should serve as nodes for urban residents [3] ; Professor Li Deren, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Engineering, believes that a smart city is an intelligent urban management and operation model that is visualized and measurable, built upon a fully digitalized urban foundation, and integrates digital cities with the Internet of Things [4] . This design comprehensively uses the latest prefabricated technology and information technology, etc., to provide a more efficient, green, and intelligent planning and design for urban transformation.
2 Design Philosophy
This design proposal starts with the city as the basis and undertakes a disruptive creation in multiple aspects such as transportation, environment, functional support, and residential life. It relies on implementable modern scientific and technological advancements and integrates them for comprehensive application in urban construction. This can provide new feasible suggestions for solving common urban issues such as traffic congestion, deterioration of the ecological environment, and outdated living facilities.
2.1 Efficient Cities
To address traffic congestion during peak hours such as commute times, this design fully takes advantage of underground space to create a three-dimensional transportation system, allowing surface areas to be designated for pedestrians and achieving city-level separation of pedestrians and vehicles. This solution can significantly reduce traffic congestion and the likelihood of traffic accidents. To efficiently use urban land and achieve a balance between work and residence, this design adopts different spatial levels to set appropriate functions, creating a comprehensive community that integrates living, entertainment, office, services, business, and commerce, truly achieving a work-life balance. The underground space serves as parking and commercial support services, with residential units on the south side above ground, and the north side designated for community support services such as property management, activity centers, elder care facilities, kindergartens, gyms, libraries, co-working spaces, business clubs, etc., truly achieving an intelligent, efficient, and convenient modern smart city.
2.2 Ecological Cities
Based on the concept of a green city where humans and nature coexist harmoniously, to build a green and livable city that harmonizes with nature, this design raises the base level of buildings to minimize their footprint, allowing more land to be devoted to greenery. Motor traffic is placed underground, and there is a true sense of open community, integrating community parks with city parks into a cohesive whole. The design incorporates cascading terraces to create vertical forests and strongly advocates for the use of solar power and new energy vehicles.
2.3 Smart Cities
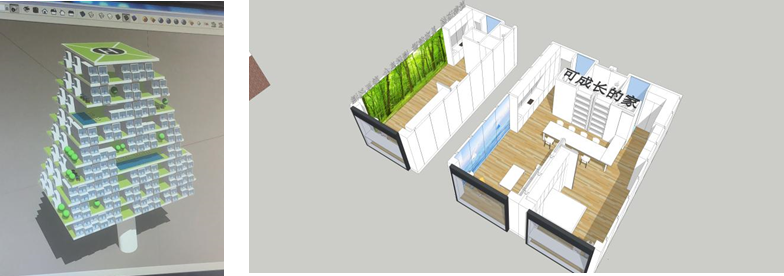
Leveraging modern information technology, this design aims to build an intelligent smart city to enhance the living efficiency of urban residents. For example, houses that automatically rotate to adjust their orientation according to different climatic conditions, ensuring they always face the optimal direction; smart security systems and facial recognition systems to realize open communities; smart home technologies; prefabricated buildings that can grow with the family, allowing flexible modular combinations based on the structure of family members; homes that can travel with you, utilizing the concept of parking buildings, enabling us to take our homes to the cities we wish to work or travel in.
2.4 Open and Shared Cities
To maximize resource utilization and build a sustainable smart city, this design incorporates living support circles, shared city parks, shared terraced areas, and shared office spaces on the north side to create an open and shared city. This approach also provides a foundation for building a harmonious social and humanistic environment for urban residents.
2.5 People-Centric, Culturally Rich Cities
This design focuses on people-centric, culturally rich development through the construction of elderly centers, kindergartens, health archives, and public activity centers.
A smart city, thriving in light, aims to create real homes in the park, returning the outdoors to nature, embodying smart cities, ecological communities, cultural communities, new energy, prefabricated technology, and work-life balance
3 Feasibility Analysis of the Proposal
This design primarily relies on current mature technologies.
3.1 Prefabricated Construction
Currently, prefabricated construction technology is very mature. It has been prevalent for many years in developed regions such as Europe, America, and Japan. In China, prefabricated construction has become a key direction for transformation in the construction industry.
3.2 Smart Technology
The smart recognition systems, induction charging systems, and smart home systems mentioned in this proposal are all mature technologies that have already been implemented in real-world scenarios.
3.3 Rotatable Houses
Making houses rotate is a concept that exists globally, similar to the revolving restaurant in the Oriental Pearl Tower, which can rotate 360 degrees.
3.4 Cantilever Structures
The biggest challenge of this design is the cantilevered ground floor, with only one structural core tube supporting the entire building. Similar structures exist, such as various television towers around the world.
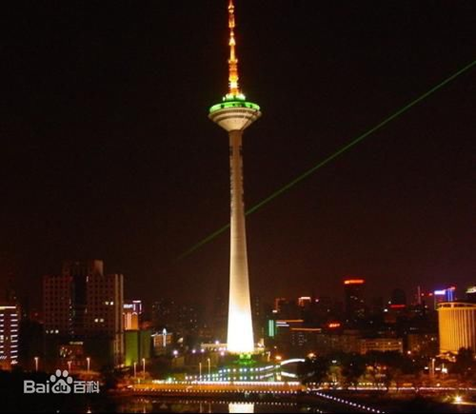

Figure 1: Example of a Television Tower
4 Production
By refining the three-dimensional model, a visually strong spatial model is formed, which guides the creation of the physical model.

Figure 2: Building Unit + Underground Space + Urban Space Form the Minimal Conceptual Model

Figure 3: The architectural model features cascading terraces and north-south zoning for efficient greening
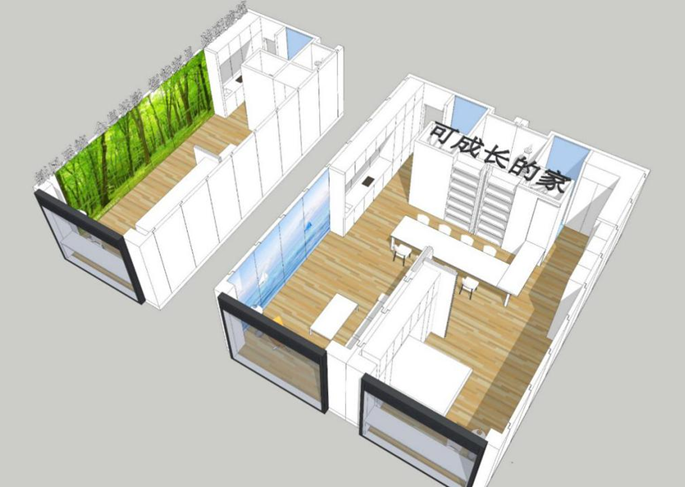

Figure 4: Construction of residential unit models, and freely combinable collage models
5 Conclusion
This design provides an efficient, green, and smart planning concept. Models have already been created for this design, and all technologies used are currently mature scientific technologies, offering practical reference!
6 Outlook
This project is currently undergoing various structural engineering analyses to determine the required strength and types of construction materials, along with actual budget analyses and other tasks. It is hoped that this type of design can be transformed into reality, turning urban construction into green, smart, efficient, and livable new cities. To realize Smart City, Thriving in Light.
The image above shows a model of the smart city design.

The image above features Hua Hongyang and the smart city.

The image above shows Hua Hongyang speaking on behalf of the team at the first Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao (International) Youth Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition.

The image above shows Hua Hongyang being interviewed by Beijing Television News Channel.
The presentation PPT for the entire project is as follows.

(the First Prize for the first Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao (International) Youth Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition)

(the Third Prize for the 39th Beijing Youth Science Creation Competition)
The image above shows the award certificate